View Indexes for N1QL
Just like GSIs, Views for N1QL supports a variety of OLTP like use-cases including basic, ad-hoc, and short-running reporting queries that require filtering and aggregations.
Views are deployed into the data service as a local index within the Couchbase Server cluster, aligned with data service distribution. Views provide the following advantages:
-
Auto Partitioning of Indexes: Views come with auto partitioning and smart placement within the data service.
-
Built-in replicas and HA for Indexing: Views come with built in replicas for high availability within the data service including Server Group Awareness support and rebalance support.
-
Simple Scaling Model: Views are automatically placed and scaled with the data service.
Creating Views for N1QL
You can define a primary or secondary index using Views for N1QL using the CREATE INDEX statement and USING VIEW clause. For more information on the syntax and examples, see CREATE INDEX statement.
Placement of Views
Data nodes hash partition data so that data is uniformly distributed across the cluster. View indexes are co-located with the data and each view index contains only a subset of the data that is available on the node.
Views Performance
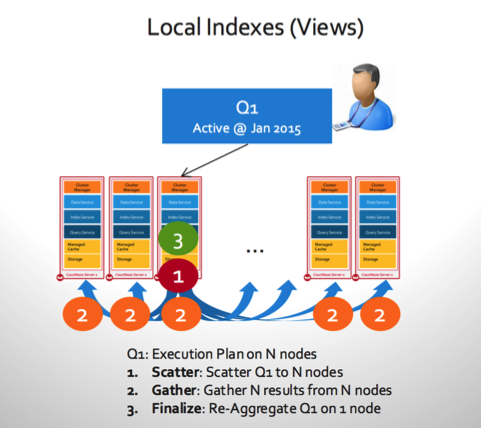
Views require scatter-gather to execute scans due to its architecture. View is a local index that is placed aligned with data distribution in the data service.
Query and View Consistency
In Couchbase Server, mutations to data in the data service is done with full consistency. (All mutations to a given key is done using the same vBucket on a node and is immediately available to anyone reading the latest value for the given key). However, views are maintained in an eventually consistent manner. This is true for all indexers (GSI, View and Spatial). At query time, you can specify a query consistency flag for each N1QL query request, similar to the view API. The query consistency flag can be one of the following:
-
not_bounded: This scan_consistency flag executes the query immediately without requiring any consistency for the query. If the view maintenance is running behind, query may return out-of-date results. This consistency flag is identical to thestale=okconsistency flag used in the View Query API -
request_plus: This scan_consistency flag executes the query but require the indexes to be updated to the logical timestamp of the query request. For example, an application issuing the query may have done its last update 100 ms ago. An application issuing the query with request_plus scan consistency flag takes the logical timestamp of query request. This behavior achieves consistency, at least or later than the moment of the request timestamp. If the view maintenance is running behind the request timestamp, the query waits for the view to catch up to the request timestamp. This consistency option is identical to thestale=falseconsistency flag used in the View Query API.
For N1QL, the default consistency setting is not_bounded.